SEO is all about directing users to your website pages that fit their needs and solve their problems.
Sometimes you might need to relocate some content to a different webpage or another section of your website.
Even more, you might rebrand and use a different domain. In such cases and for other reasons, users might not be able to access your content using the old page.
This is where SEO redirects are crucial so you don’t lose these users and provide a better user experience and faster access to the information the visitors are looking for.
In this article, we will go through everything you need to know about SEO directs and why you need to use a redirect checker for better SEO results.
What is a Redirect?
A redirect is a code responsible for sending users and bots to a different URL than the one actually clicked or requested without the users noticing or realizing it.
In simpler words, a redirect is forwarding one URL to another URL directing traffic to the new destination.
Why Should You Use Redirects?
As a website owner, your website is constantly evolving which means that the content gets updated, webpages get moved, and URLs change.
SEO redirects are essential to maintaining the integrity of your website’s structure and ensuring a seamless user experience.
Here’s why you should incorporate SEO redirects into your digital strategy:
- Preserving past SEO efforts: When a webpage undergoes changes such as URL modifications or content updates, failing to implement redirects can result in broken links and lost SEO value.
Redirects help preserve the SEO equity accumulated by the original URL, ensuring that search engines recognize and credit the new destination appropriately. - Enhancing User Experience: Imagine clicking on a link, only to be met with a 404 error page. It’s not just frustrating for users; it also affects your website’s credibility and professionalism.
Use redirects to seamlessly guide users to the correct destination and prevent confusion and frustration. - Maintaining Backlink Integrity: Backlinks are valuable off-page SEO assets. They contribute to your website’s domain authority and ranking. When you change URLs without implementing redirects, you risk losing valuable backlinks as well.
Redirects ensure that links continue to point to the relevant content, preserving their SEO value and saving external traffic. - Facilitating Website Changes: Whether you’re restructuring your website, merging pages, deleting some pages, or launching a new domain, redirects are essential for facilitating these changes smoothly.
Instead of leaving users abandoned on outdated or non-existent pages, redirects guide them to the new and improved content, ensuring a seamless transition. - Adapting to Search Engine Algorithms: Search engines like Google prioritize user experience and content relevance when determining search rankings.
Websites that deliver a seamless browsing experience, free of broken links and outdated content, are more likely to rank higher in search results.
By using redirects to maintain a well-organized and user-friendly website, you can align with search engine algorithms and improve your chances of ranking success.
When Should You Use Redirects?
Now that you understand the definition of redirects and the benefits of implementing them, here are some usage cases of when you need to use redirects.
1- Moving Content to a New URL
When you make changes to your website’s content or the URL structure, such as updating page titles, or modifying permalinks, redirects should be used to guide users and search engines to the new locations.
This ensures that visitors can still access the desired content, and SEO equity from the old URLs is preserved.
2- Deleting a Page
If for any reason you need to delete a webpage, you should utilize redirects to prevent customers from landing on an empty page with a 404 page-not-found error.
A redirect creates a better user experience and gives the visitors an alternative instead of bouncing. It also protects your business image from looking non-credible and unprofessional.
3- Moving Your Site to a New Domain or Rebranding
If you are moving your website to a new domain due to the loss of the old domain after expiration or if you want to change it slightly from .net to .com. You might also be rebranding where you will change the name of your business and you will need a new domain matching the new name.
Place redirects to send visitors to the new domain and save your website visibility and your past SEO value.
4- Rebuilding Your Site Structure
If you are restructuring your website and rearranging the content categories and the website menus you will need to use redirects.
This can be part of arranging your blog content, your e-commerce product pages, or any other restructuring process. Your end goal here is to never leave an old webpage/URL without a redirect to the updated destination.
5- Websites and Page Consolidation
If you have multiple websites or multiple web pages with similar content and you wish to consolidate them into a single destination, place redirects to redirect traffic from the redundant pages and website to the consolidated one.
Redirects in this case will concentrate on the SEO value and prevent keyword cannibalization.
6- Canonicalization
Canonicalization is the process of specifying the preferred version of a webpage when multiple versions exist. For example, if your website has both “www” and “non-www” versions, or HTTP and HTTPS versions, you should use redirects to canonicalize URLs and ensure that search engines index the preferred version.
7- Running a Promotion
Use a redirect during promotions to send visitors to your promotion landing page instead of the standard product page. For example, place a redirect to guide users to websitename.com/product-black-friday-sale instead of websitename.com/product.
8- Resolving Minor URL variation issues
an upper-case variation from the lower-case version of the URL will lead to a different page. For example, website.com/OFFERS vs website.com/offers. Even one capitalized letter in a URL can make it different from its all-lower-case counterpart.
Also, a trailing slash can do the same thing. For example, website.com/offers/ instead of website.com/offers.
Utilize redirects to make sure you benefit from all the traffic coming into your website and for Google to better index all these variations pages.
9- Temporary Changes
In some cases, you may need to temporarily redirect traffic from one URL to another, such as during website maintenance or A/B testing.
Temporary redirects (we will be discussing them later) should be used for such scenarios to indicate that the move is temporary and preserve the original URL’s SEO value.
Types of Redirects
There are several types of redirects, each serving a specific purpose in directing web traffic from one URL to another.
Understanding the differences between these redirect types is essential for implementing them effectively in various scenarios.
Here are the primary types of redirects:
1- 301 Redirect (Moved Permanently)
The 301 redirect is used to indicate that a webpage has permanently moved to a new location. It informs search engines that the original URL has been replaced by a new one.
301 redirect passes the SEO value such as link equity (also known as link authority or link juice) and ranking signals from the old URL to the new one. Therefore, assigning a 301 status code to an old post with good page authority and high traffic is a good SEO technique.
301 redirects are ideal for permanent changes, such as URL restructuring, content migrations, consolidation, or website rebranding.
2- 302 Redirect (Found or Moved Temporarily)
The 302 redirect is used to indicate that a webpage has temporarily moved to a different location.
Unlike the 301 redirect, the 302 redirect does not pass the SEO value from the original URL to the new one.
It is often used for temporary changes or testing purposes, as it allows the original URL to retain its SEO value while the temporary redirect is in place.
You can use this during website maintenance, split testing, and promotions.
3- 307 Redirect (Temporary Redirect)
Similar to the 302 redirect, the 307 redirect indicates that a webpage has temporarily moved to a new location. It is more explicitly defined in HTTP/1.1 and serves the same purpose as the 302 redirect.
Like the 302 redirect, the 307 redirect does not pass SEO value from the original URL to the new one and is suitable for temporary changes.
While the major web crawlers may treat a 307 redirect similarly to a 302 redirect in some cases, it is recommended to use a 301 redirect for permanent changes and a 302 redirect for temporary changes.
4- Meta Refresh Redirect
Meta refreshes are a type of redirect executed on the page level instead of the server level.
Meta refresh redirects are implemented using HTML meta tags within the webpage’s code.
They automatically redirect users to a new URL after a specified time delay. Meta refresh redirects are less commonly used for SEO purposes due to their limitations and potential impact on user experience.
5- 404 Error Redirect
It is best to utilize 301 redirects when a page is deleted to avoid 404 errors. However, if for any reason you want to be extra safe if any deleted page has no redirect for it, and also for situations where the URL was typed in incorrectly, add a 404 error redirect.
A 404 customized redirect can send the user back to the main site or a specific webpage instead of reaching a dead end. This way you can avoid losing traffic to your site.
Best SEO practices for redirects
1- Use 301 Redirects for Permanent Changes
As we explained above, 301 redirects save the SEO value or what is referred to as link equity, link authority, or link juice.
That’s why you should use a 301 redirect when you are permanently moving content to a new destination to inform search engines that the original URL has permanently moved and to preserve the search ranking.
301 redirects also provide a smooth transition for visitors creating a better user experience.
2- Utilize 302 Redirects for Temporary Changes
For temporary content moves or changes, such as during website maintenance, testing, or promotions, use a 302 redirect to indicate that the move is temporary.
This way the search engines won’t pass SEO value from the original URL to the new one, making them suitable for temporary changes that do not affect long-term SEO goals.
3- Avoid Redirect Chains
Redirect chains happen when instead of directing the users to the new desired destination right away, you send them and search engines through a chain of multiple intermediary URLs before they finally arrive at the final destination.
Avoid redirect chains and instead implement redirects directly from the original URL to the final destination without unnecessary intermediary steps.
4- Fix Redirect Loops
Redirect loops occur when two or more URLs redirect to each other in an infinite loop or when a URL within a redirect chain directs to a URL earlier in the chain.
Redirect loops prevent users and search engines from reaching the desired content, causing bad user experience, loss of traffic, and bad ranking.
Regularly monitor for redirect loops and promptly resolve them by adjusting redirects to ensure they point to the correct destinations without creating a loop or a chain of unnecessary stops.
5- Update Internal Links and Sitemaps
When implementing redirects, don’t forget to update the internal links in your website content and also update the navigation menus to point to the new URLs.
Additionally, update your website’s XML sitemap to include the new URLs and remove references to any redirected URLs.
This practice enables search engines to crawl and index your updated content correctly for better SEO results.
6- Monitor and Test Redirects Regularly
Regularly monitor your website’s redirects using a redirect checker. Test redirects to ensure they are functioning correctly and directing users and search engines to the intended destinations without errors, loops, or chains.
What is a Redirect Checker?
To complete the last step we mentioned of the SEO redirects best practices you need to use a redirect checker.
A redirect checker is a tool or software that helps you verify and analyze the redirections of URLs.
By using a redirect checker you can determine whether a particular URL is redirecting correctly or not, and where it redirects to and quickly identify issues, errors, redirect loops, and redirect chains.
Why Do You Need a Redirect Checker?
We use SEO Minion which is a redirect checker that also offers other on-page SEO and SERPs analysis.
Here is what you can achieve using the redirect checker SEO Minion:
- A redirect checker helps you find redirects on your website pages and check their destination to ensure that it is the right one with no loops or unnecessary chains.
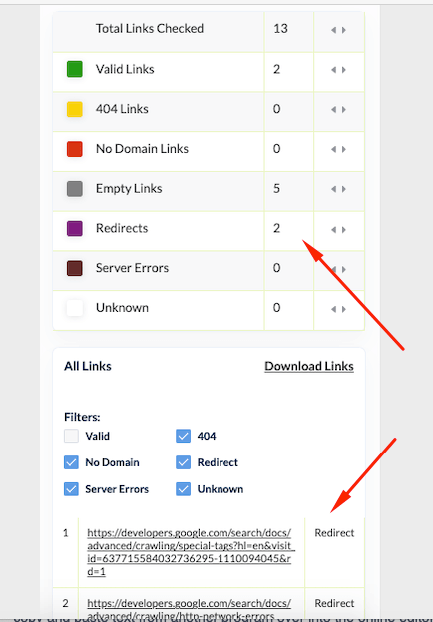
- Locate any 404 errors and broken links quickly by using a redirect checker so that you can place a redirect to stop traffic losses and improve the user experience.
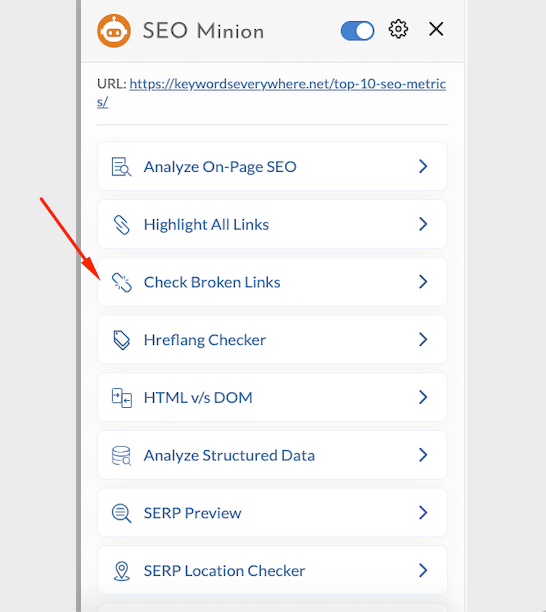
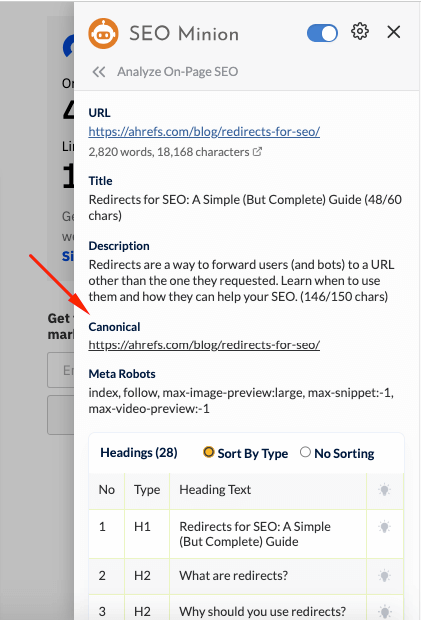
- Check if there is a canonical added or if you need to add one because there are multiple versions of the webpage.
- A redirect checker saves you time and effort. Manually checking and analyzing redirects across a website can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.
A redirect checker automates the process, saving you both time and effort so you can focus directly on solving any issues and making any improvements.
Final Thoughts
Redirects are a critical aspect of website management and SEO to ensure your visitors are finding the content they need on your website.
By understanding how redirects work, their types, when to use them, and best SEO practices for implementation, you can maintain a smooth user experience and preserve SEO value.
Additionally, using tools like SEO Minion redirect checker can streamline the process and help you identify and fix redirect issues efficiently and instantly.


